Turing Machine:
A Turing machine is a computational model, like Finite Automata (FA), Pushdown automata (PDA), which works on unrestricted grammar. The Turing machine is the most powerful computation model when compared with FA and PDA.
The Turing Machine (TM) is the machine level equivalent to a digital computer.
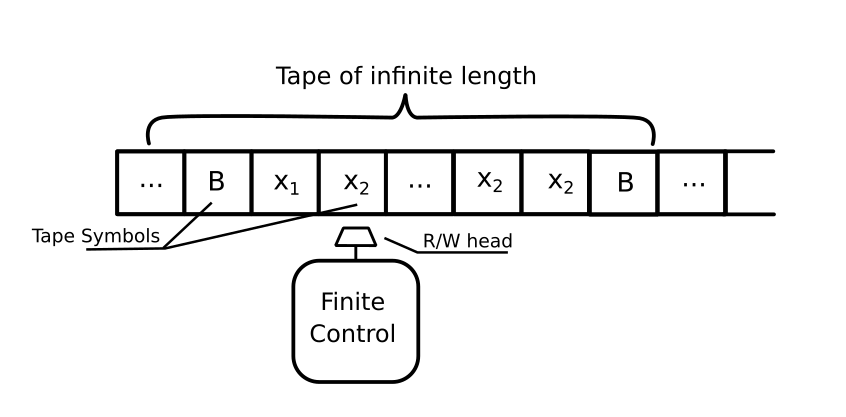
A single tape Turing machine has a single infinite tape, which is divided into cells. The tape symbols are present in these cells.
A finite control is present, which controls the working of Turing machines based on the given input.
The Finite control has a Read/write head, which points to a cell in tape.
A Turing machine can move both left and right from one cell to another.
Turing machine can be defined using 7-tuple:

Parity Checking:
Parity checking, which was created to eliminate data communication errors, is a simple method of network data verification and has an easy and understandable working mechanism.
A parity check is a process that ensures accurate data transmission between nodes during communication.
A parity bit is appended to the original data bits to create an even or odd bit number; the number of bits with value one.
The source then transmits this data via a link, and bits are checked and verified at the destination.
Data is considered accurate if the number of bits (even or odd) matches the number transmitted from the source.
Turing Machine:

Online Simulator:
Site: https://turingmachine.io/
Code:
input: '1011001'
blank: ' '
start state: q0
table:
q0:
1 : {write: 1, R: q1}
0 : {write: 0, R: q0}
q1:
1 : {write: 1, R: q2}
' ' : {write: 1, R: q3}
0 : {write: 0,R: q1}
q2:
1 : {write: 1,R: q1}
0 : {write: 0,R: q2}
' ' : {write: 0,R: q3}
q3:State Diagram:

Python Implementation:
Turing Machine Code:
source: https://python-course.eu/applications-python/turing-machine.php
class Tape(object):
blank_symbol = " "
def __init__(self,
tape_string = ""):
self.__tape = dict((enumerate(tape_string)))
# last line is equivalent to the following three lines:
#self.__tape = {}
#for i in range(len(tape_string)):
# self.__tape[i] = input[i]
def __str__(self):
s = ""
min_used_index = min(self.__tape.keys())
max_used_index = max(self.__tape.keys())
for i in range(min_used_index, max_used_index):
s += self.__tape[i]
return s
def __getitem__(self,index):
if index in self.__tape:
return self.__tape[index]
else:
return Tape.blank_symbol
def __setitem__(self, pos, char):
self.__tape[pos] = char
class TuringMachine(object):
def __init__(self,
tape = "",
blank_symbol = " ",
initial_state = "",
final_states = None,
transition_function = None):
self.__tape = Tape(tape)
self.__head_position = 0
self.__blank_symbol = blank_symbol
self.__current_state = initial_state
if transition_function == None:
self.__transition_function = {}
else:
self.__transition_function = transition_function
if final_states == None:
self.__final_states = set()
else:
self.__final_states = set(final_states)
def get_tape(self):
return str(self.__tape)
def step(self):
char_under_head = self.__tape[self.__head_position]
x = (self.__current_state, char_under_head)
if x in self.__transition_function:
y = self.__transition_function[x]
#print(self.__tape,self.__head_position)
self.__tape[self.__head_position] = y[1]
if y[2] == "R":
self.__head_position += 1
elif y[2] == "L":
self.__head_position -= 1
self.__current_state = y[0]
def final(self):
if self.__current_state in self.__final_states:
return True
else:
return False
Parity Checking Using Turing Machine:
initial_state = "q0",
accepting_states = ["q1","q2","q3"],
transition_function = {("q0","0"):("q0", "0", "R"),
("q0","1"):("q1", "1", "R"),
("q1","0"):("q1", "0", "R"),
("q1","1"):("q2", "1", "R"),
("q1","_"):("q3", "1", "R"),
("q2","0"):("q2", "0", "R"),
("q2","1"):("q1", "1", "R"),
("q2","_"):("q3", "0", "R")
}
final_states = {"q3"}
string = "1011001__"
t = TuringMachine(string,
initial_state = "q0",
blank_symbol="_",
final_states = final_states,
transition_function=transition_function)
print("Input on Tape:\n" + t.get_tape())
while not t.final():
t.step()
print("Result of the Turing machine calculation:")
print(t.get_tape())
Output:

Get contents delivered to your mail ID by entering your mail ID on the HOME page.


















































